
It is acceptable to visualize light rays as laser rays (or even science fiction depictions of ray guns).Įxplain that light bounces is a simplification. Here it means a straight line that originates from some point. It then continues in a straight line-that is, as a ray.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)
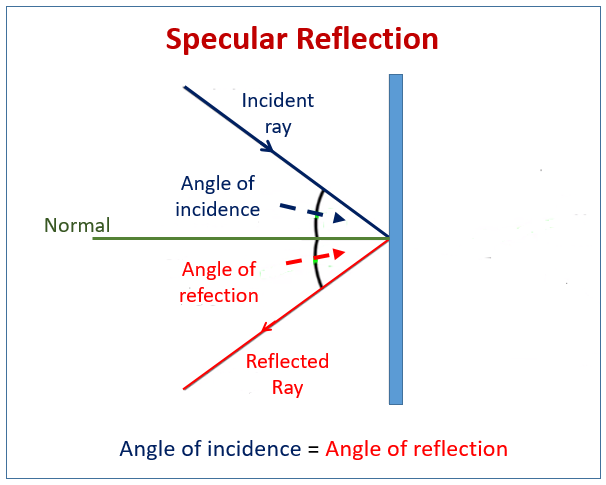
Light may change direction when it encounters the surface of a different material (such as a mirror) or when it passes from one material to another (such as when passing from air into glass). In all these cases, light is modeled as traveling in a straight line, called a ray. Light can also arrive at an object after being reflected, such as by a mirror. Light can travel to an object through various media, such as air and glass. It can come directly from the source through empty space, such as from the Sun to Earth. There are three ways, as shown in Figure 16.2, in which light can travel from a source to another location. There are six possible ratios therefore, there are six such functions. Trigonometric functions are ratios of the lengths of two sides of a right triangle. In this chapter, we apply equations that use trigonometric functions that describe the properties of angles. In this chapter, we are focused on the first three ideas. Geometry is the study of relationships involving points, lines, angles, and shapes. The lines must be straight lines for the number to have meaning. Recall that, in geometry, angles are numbers that tell how far two straight lines are spread apart. (D) investigate behaviors of waves, including reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, resonance, and the Doppler effect.

Angle of reflection definition manual#
In addition, the High School Physics Laboratory Manual addresses content in this section in the lab titled: Mirrors and Lenses, as well as the following standards:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
